Abraham H. Maslow (1908–1970) was arguably one of the most significant psychologists of modern world. The hierarchy of human needs outlined by Maslow (1943, 1954) is one of his most stable contributions to psychology (Rivera, 2006). Distinctively Maslow theorized that people have five types of needs and that these needs are activated in a hierarchical manner (Kaur, 2013).Kritsonis (2002) emphasizes that according to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory, an individual’s needs are prearranged in a hierarchical order the lower-level physiological needs to the higher-level needs for self-actualization. The physiological needs are the highest precedence because until they are sensibly satisfied, other higher-level needs will not appear to stimulate behavior.
The initial and most extensive edition of Maslow's hierarchy of needs includes five motivational needs, often represented as hierarchical levels within a pyramid (McLeod, 2007).
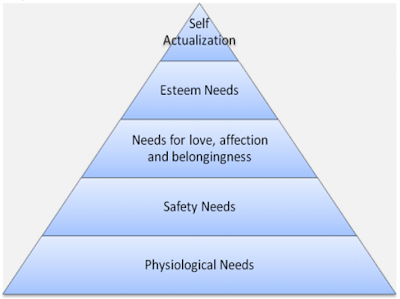
(Source: Macleod, 2007)
The deficit of basic needs are said to motivate people when they are not met. Also, the need to accomplish such needs will become stronger the longer the period they are deprived of. For instance, the longer a person goes without food the more hungry they will become with the longing and the frustration they go through. Every person is capable and has the desire to move up the hierarchy toward a level of self-actualization to feel accomplished. Regrettably, improvement is often interrupted by failure to meet lower level needs. Life experiences including divorce and loss of job may cause an individual to vary between stages of the hierarchy (McLeod, 2007).
Instead of focusing on psychopathology and what goes wrong with people, Maslow invented a more positive account of human actions which focused on what goes right. He was fascinated in human potential, and how we realize that potential. Psychologist Maslow stated that human motivation is based on people seeking accomplishment and change through personal growth. Self-actualized people as those who were fulfilled and doing all they were capable of. The growth of self-actualization person refers to the need for personal growth that is available throughout a person’s life. For Maslow, a person is always “becoming” and never remains stagnant in these terms. In self-actualization a person comes to find a sense to life that is important to them. As each person is unique the motivation for self-actualization guide people in different directions (Kenrick et al., 2010). For some people self-actualization can be realized through creating works of art or literature, for others through sport, in the classroom, or within a corporate setting.
Human Resource Management (HRM) plays a key role in managing the most important asset in an organization and HRM is known as a multidisciplinary organizational task that draws theories and ideas from diverse fields such as management, psychology, sociology and economics (Storey, 1992). Aimed at developing people through work (Bratton and Gold, 2001), human resource management includes managerial activities that are associated with planning, recruitment, selection, orientation, training, assessment, motivation and compensation (Storey, 1992).
Unlike any other asset in an organization, human asset requires motivation which has a larger impact on employee performance which is a key element required in achieving organizational goals. Hence, employee’s performance is an issue that has received broader interest in literature and research due to its significance since every organization aims to achieve superlative performance (Ojo, 2009). Performances are activities that guarantee goals are constantly being met in an effective and efficient manner (Cardy and Selvarajan, 2004; McNamara 2005). Employee’s performance refers to the recognizable behaviors and actions which explicate how a job is done, plus the results that are anticipated for adequate job performance (McNamara, 2005).
Maslow wanted to recognize what motivates people. He assumed that individuals hold a set of motivation systems isolated to rewards or insensible desires. (McLeod, 2007) Maslow stated that people are motivated to achieve particular needs. When one need is fulfilled a person would search to fulfill the next one, and so on. Desire to understand this aspect, made him to investigate and come up with the Self-Actualization Model which was discussed before.
Also, Motivational factors play a significant role in increasing employee job satisfaction. This will lead to improved organizational performance. High productivity is a long term payback of employee motivation. Motivated employee is a valuable asset who generates value for an organization in amplifying the business and revenue growth (Kaur, 2013).
According to various literatures on motivation, individuals often have problems in identifying what they want from a job. Therefore, employers have ignored what individuals’ say that they want, instead telling employees what the employer wants, based on what managers believe most people want under the circumstances. These decisions have predominantly been based on Maslow's needs hierarchy, including the factor of prepotency. As a person go forward through an organization, his employer supplies or provides prospects to satisfy needs higher on Maslow's pyramid (Gawel, 1997).
Organization remuneration can also play a major role in an employee's satisfaction and higher job performance. Some organizations offer bonuses or extra benefits to certain employees who attempt to improve their performance year by year. This can include coaching, mentoring, training or allocations to attend specialized conferences. These sorts of secondary benefits can stimulate an employee to take on new opportunities to improve themselves and, as a result, improve his or her performance in their current position which will eventually befit the employee to progress. It can also set his or her career path in a better direction, for future development and promotion (McNamara, 2005). The method an organization chooses for performance appraisals and evaluations can have the biggest effect on employee performance. Organizations that fail to review their employee's performance or recognize a job well done may soon find dissatisfied employees who will then be responsible for the lower performance of the organization. Furthermore, organizations that rigorously monitor employee work without providing employees the opportunity to provide feedback may also result in non-motivated employees (Cardy and Selvarajan, 2004).
My experience lays with one of the leading commercial banks in Sri Lanka and it is more or less of a Small and Medium Enterprises focused bank in the financial industry. If the employee grades of the subjected organization are arranged according to the Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, the organizational structure would look like below:

Factors Explanation
- Physiological needs are the need at the base of the triangle and include the lowest order need and most fundamental. This includes the need to satisfy the elementary biological drives such as food, air, water and shelter (Kaur, 2013). They are the strongest needs because if a person were deprived of all needs, it is these physiological ones that would emerge first in the person's search for fulfillment (Jerome, 2013).According to Maslow organizations must provide employees with a salary that facilitate them to afford tolerable living conditions. The underlying principle here is that any hungry employee will barely be able to make much of any contribution to his organization (Kaur, 2013).
- Safety needs: this inhabit the second level of needs. Safety needs are triggered after physiological needs are met (Kaur, 2013). When all physiological needs are satisfied and are no longer controlling thoughts and behaviors, the needs for security can become active. While adults have little consciousness of their security needs except in times of an urgent situation or periods of disorganization in the social configuration (such as common rioting), children often exhibit the signs of uncertainty and the need to be safe (Jerome, 2013). They refer to the need for a secure functioning environment free from any intimidation or harms. The basis is that employees working in an environment free of harm do their jobs without trepidation of harm (Kaur, 2013).
- Social needs: This symbolizes the third level of needs. They are activated after safety needs are satisfied (Kaur, 2013).These comprise the longing for fondness, belongingness, recognition, and friendship. These are concerned with an individual’s capability to exist in agreement with other people (Adiele & Abraham, 2013). Maslow affirms that people seek to overcome feelings of loneliness and disaffection. This involves both giving and receiving love, recognition, affection and the sense of belonging (Jerome, 2013).
- Esteem needs: This is explained in the fourth level of needs. It includes the need for self-worth and endorsement of others (Kaur, 2013). These involve needs for both self-esteem and for the esteem a person gets from others. Humans have a need for a steady, firmly based, high level of self-respect, and revere from others. When these needs are satisfied, the person sense self-confident and valuable as a person in the world (Jerome, 2013).But when they are not satisfied; it fabricates feelings of vulnerability and inferiority (Adiele & Abraham, 2013),
- Self-actualization: This is the last level at the top of the triangle. This refers to the need to become all that one is competent of being to grow ones maximum potential (Kaur, 2013). This means to become more and more what is required for one to become everything that a person is capable of becoming (Adiele & Abraham, 2013). The underlying principle here holds to the position that self-actualized employees embody valuable resources to the organization human resource (Kaur, 2013).
The deficit of basic needs are said to motivate people when they are not met. Also, the need to accomplish such needs will become stronger the longer the period they are deprived of. For instance, the longer a person goes without food the more hungry they will become with the longing and the frustration they go through. Every person is capable and has the desire to move up the hierarchy toward a level of self-actualization to feel accomplished. Regrettably, improvement is often interrupted by failure to meet lower level needs. Life experiences including divorce and loss of job may cause an individual to vary between stages of the hierarchy (McLeod, 2007).
Examples
- Physiological Needs: The well-known Googleplex command center in Mountain View, California, offers outwardly endless free food choices. Employees can eat every meal free at the campus restaurants and cafes—and save a ton of money savings as well as for their future endeavors (Money, 2018).
- Safety Needs: The coffee chain is known for treating its employees well. Starbucks offers full reimbursement of tuition for those who are willing to do their higher studies (Money, 2018).
- Social Needs: Airbnb wants employees to enjoy travelling around the world as much as its customers. The holiday rental listing site offers staff an annual $2,000 remuneration to fly around the world and stay in an Airbnb spot anywhere (Money, 2018).
- Esteem Needs: Despite media attention paid to commercial jet travel, many CEOs are provided with ground transport bonus including company cars, privileged parking or a car and driver. According to MarketWatch, the tab for car and driver service provided to Macy's Inc. CEO Terry Lundgren topped $261,000 in 2009 (Investopedia, 2018).
- Self-actualization: Bill Gates, who has held the title of “World’s Richest” human for 15 of the last 20 years, has given away more than any living person. In 2010, Gates and Warren Buffett announced “The Giving Pledge”- a campaign for billionaires to commit to giving a bulk of their billions to charitable causes (Complex, 2018).
Self-Actualization
Link between Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs and Employee Motivation
Unlike any other asset in an organization, human asset requires motivation which has a larger impact on employee performance which is a key element required in achieving organizational goals. Hence, employee’s performance is an issue that has received broader interest in literature and research due to its significance since every organization aims to achieve superlative performance (Ojo, 2009). Performances are activities that guarantee goals are constantly being met in an effective and efficient manner (Cardy and Selvarajan, 2004; McNamara 2005). Employee’s performance refers to the recognizable behaviors and actions which explicate how a job is done, plus the results that are anticipated for adequate job performance (McNamara, 2005).
Maslow wanted to recognize what motivates people. He assumed that individuals hold a set of motivation systems isolated to rewards or insensible desires. (McLeod, 2007) Maslow stated that people are motivated to achieve particular needs. When one need is fulfilled a person would search to fulfill the next one, and so on. Desire to understand this aspect, made him to investigate and come up with the Self-Actualization Model which was discussed before.
Also, Motivational factors play a significant role in increasing employee job satisfaction. This will lead to improved organizational performance. High productivity is a long term payback of employee motivation. Motivated employee is a valuable asset who generates value for an organization in amplifying the business and revenue growth (Kaur, 2013).
According to various literatures on motivation, individuals often have problems in identifying what they want from a job. Therefore, employers have ignored what individuals’ say that they want, instead telling employees what the employer wants, based on what managers believe most people want under the circumstances. These decisions have predominantly been based on Maslow's needs hierarchy, including the factor of prepotency. As a person go forward through an organization, his employer supplies or provides prospects to satisfy needs higher on Maslow's pyramid (Gawel, 1997).
Organization remuneration can also play a major role in an employee's satisfaction and higher job performance. Some organizations offer bonuses or extra benefits to certain employees who attempt to improve their performance year by year. This can include coaching, mentoring, training or allocations to attend specialized conferences. These sorts of secondary benefits can stimulate an employee to take on new opportunities to improve themselves and, as a result, improve his or her performance in their current position which will eventually befit the employee to progress. It can also set his or her career path in a better direction, for future development and promotion (McNamara, 2005). The method an organization chooses for performance appraisals and evaluations can have the biggest effect on employee performance. Organizations that fail to review their employee's performance or recognize a job well done may soon find dissatisfied employees who will then be responsible for the lower performance of the organization. Furthermore, organizations that rigorously monitor employee work without providing employees the opportunity to provide feedback may also result in non-motivated employees (Cardy and Selvarajan, 2004).
Experiential Learning

According to the present HRM practice in the organization where I am working in, following benefits are provided to the two bottom level staff member grades which falls under Physiological Needs and Safety Needs quadrant , which includes fuel allowance, lunch at a one fifth of the price, consumption, housing, personal and vehicle loans at a lower interest rates, job related local training, holiday allowance, spectacle claims, Out Patient (OPD) allowance, hospitalization and life insurance cover apart from the usual basic remuneration, employee provident fund and employee trust fund pay outs. The set of aforementioned benefits pretty much covers the basic needs of any human being. Certainly at this level, mentioned facilities work as a motivational factor for the human resource of the organization which leads to a better job performance.
In an institution like a Bank, said benefit packages are provided across all levels of employees and the only difference is that, the value of the entitlements are increased when employees move up in the hierarchy with some additional benefits to support the employee motivation accordingly. The tier with the social needs “Managers, Senior and Chief Managers” are offered with foreign training, company paid educational programs, in the areas of EQ,IQ and Leadership, Club memberships and entertainment allowances which encourages the respective employees to move along with the peer groups to give some scene of love and belonging.
Esteem Level Benefits are provided to the CEO, Senior DGM, DGM and AGM level members inclusive of all of the above along with unlimited fuel, drivers, company vehicles, Company apartment, reimbursement of grocery bills, fully paid vacations abroad inclusive of higher salary increments and year end bonuses.
According to Maslow’s explanations, the aforesaid benefits in my organization support the employees to keep up the motivation when they climb up the career ladder, yet the time taken to promote the staff members based on their experience, skill set, knowledge and the performance is really high which does not add much value to the employee in the long run. That is the only concern I see which does not provide 100% results out of the benefit package that offers to the employees, and this negativity has resulted in lower job performance and employee dissatisfaction at present.
According to Graham & Messner (1998) in general there are three major criticisms aimed at the need theory and other content theories of motivation. (A) There is limited experimental data to support their conclusions, (b) they presume employees are principally alike, and (c) they are not theories of motivation at all, but rather theories of job satisfaction. This was supported by the views of Nadler & Lawler (1979) in Graham & Messner (2000). Nadler & Lawler (1979) cited in Graham & Messner (2000) were also critical of the need theory of motivation. They argue that the theory makes the following impractical assumptions about employees in general that: (a) all employees are alike (b) all situations are alike and that (c) there is only one best way to meet needs. Another critic to this view was from Basset-Jones & Lloyd (2004). Basset-Jones & Lloyd (2004) presents that in general, critics of the need theory argue that it is as a result of the usual feeling of employees to take credit for needs met and dissatisfaction on needs not met.
With the explanations, research results and analysis done on the Need theory presented by Abraham Maslow, it is evident that the need theory has a direct connection towards employee motivation as considerable amount of scholars have validated despite the heavy criticism built up by fewer scholar. However, according to facts and figures gathered, it is self-explanatory that this theory has a significant impact of employee motivation of any of the organizations, which relates to organizational behavior and human resource management. Application of the Need theory in to any working environment could have being made as a result of the contribution made so far by Maslow’s Hierarchy of need theory which further proves through the prior explained experiential learning and will certainly lead towards employee motivation at work place.
Adiele , E. E. and Abraham, N.M. (2013) Achievement of Abraham Maslow’s Needs Hierarchy Theory among Teachers: Implications for Human Resource Management in The Secondary School System in Rivers State. Journal of Curriculum and Teaching, 2(1) 140-144.
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1157714.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Ayesha, H., Khalid ,W. and Khan,T.N. (2013) Relating Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs with Employee Turnover and Retention: Case Study of Local Telco. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 3(2) 51-67.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.679.8395&rep=rep1&type=pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Complex (2018) Paul Allen and Bill Gates, Co-Founders of Microsoft - The Most Charitable Tech CEOs | Complex. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.complex.com/pop-culture/2014/11/10-tech-ceos-who-are-changing-the-face-of-philanthropy/paul-allen-and-bill-gates-co-founders-of-microsoft. [Accessed 24 September 2018].
Francis, N. H. (2006) A Brief Analysis of Abraham Maslow’s Original Writing of Self-Actualizing People: A Study of Psychological Health. Doctoral forum national journal of publishing and mentoring doctoral student research, 3(1) 1-6.
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED501708.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
In an institution like a Bank, said benefit packages are provided across all levels of employees and the only difference is that, the value of the entitlements are increased when employees move up in the hierarchy with some additional benefits to support the employee motivation accordingly. The tier with the social needs “Managers, Senior and Chief Managers” are offered with foreign training, company paid educational programs, in the areas of EQ,IQ and Leadership, Club memberships and entertainment allowances which encourages the respective employees to move along with the peer groups to give some scene of love and belonging.
Esteem Level Benefits are provided to the CEO, Senior DGM, DGM and AGM level members inclusive of all of the above along with unlimited fuel, drivers, company vehicles, Company apartment, reimbursement of grocery bills, fully paid vacations abroad inclusive of higher salary increments and year end bonuses.
According to Maslow’s explanations, the aforesaid benefits in my organization support the employees to keep up the motivation when they climb up the career ladder, yet the time taken to promote the staff members based on their experience, skill set, knowledge and the performance is really high which does not add much value to the employee in the long run. That is the only concern I see which does not provide 100% results out of the benefit package that offers to the employees, and this negativity has resulted in lower job performance and employee dissatisfaction at present.
Criticisms
Conclusion
Reference List
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1157714.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Ayesha, H., Khalid ,W. and Khan,T.N. (2013) Relating Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs with Employee Turnover and Retention: Case Study of Local Telco. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 3(2) 51-67.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.679.8395&rep=rep1&type=pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Complex (2018) Paul Allen and Bill Gates, Co-Founders of Microsoft - The Most Charitable Tech CEOs | Complex. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.complex.com/pop-culture/2014/11/10-tech-ceos-who-are-changing-the-face-of-philanthropy/paul-allen-and-bill-gates-co-founders-of-microsoft. [Accessed 24 September 2018].
Francis, N. H. (2006) A Brief Analysis of Abraham Maslow’s Original Writing of Self-Actualizing People: A Study of Psychological Health. Doctoral forum national journal of publishing and mentoring doctoral student research, 3(1) 1-6.
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED501708.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Gawel, J.E. (1997) Herzberg's theory of motivation and Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation, 5(11) 1-3.
https://pareonline.net/getvn.asp?v=5&n=11 [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Investopedia (2018) CEO Benefits You Wish You Had. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/financial-edge/0510/ceo-benefits-you-wish-you-had.aspx. [Accessed 24 September 2018].
Jerome, N. (2013) Application of the Maslow’s hierarchy of need theory; impacts and implications on organizational culture, human resource and employee’s performance. International Journal of Business and Management Invention, 2(3) 39-45.
https://www.academia.edu/12099958/Application_of_the_Maslows_hierarchy_of_need_theory_impacts_and_implications_on_organizational_culture_human_resource_and_employees_performance [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Kaur, A. (2013) Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory: Applications and Criticisms. Global Journal of Management and Business Studies, 3(10), 1061-1064.
https://www.ripublication.com/gjmbs_spl/gjmbsv3n10_03.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Investopedia (2018) CEO Benefits You Wish You Had. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/financial-edge/0510/ceo-benefits-you-wish-you-had.aspx. [Accessed 24 September 2018].
Jerome, N. (2013) Application of the Maslow’s hierarchy of need theory; impacts and implications on organizational culture, human resource and employee’s performance. International Journal of Business and Management Invention, 2(3) 39-45.
https://www.academia.edu/12099958/Application_of_the_Maslows_hierarchy_of_need_theory_impacts_and_implications_on_organizational_culture_human_resource_and_employees_performance [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Kaur, A. (2013) Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory: Applications and Criticisms. Global Journal of Management and Business Studies, 3(10), 1061-1064.
https://www.ripublication.com/gjmbs_spl/gjmbsv3n10_03.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Kenrick, D. T.,Neuberg, S. L., Griskevicius, V., Becker, D. V. and Schaller, M. (2010) GoalDriven Cognition and Functional Behavior The Fundamental-Motives Framework. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 19(1) 63-67.
http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0963721409359281 [Accessed 23 September 2018].
McLeod, S. A. (2007) Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs. HCC Certificate in Counselling Skills,1(1) 1-8.
http://highgatecounselling.org.uk/members/certificate/CT2%20Paper%201.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Money (2018) | Money. [ONLINE] Available at: http://time.com/money/4972232/12-companies-with-the-most-luxurious-employee-perks/. [Accessed 24 September 2018].
Rivera, M.E.K. (2006) Rediscovering the Later Version of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Self-Transcendence and Opportunities for Theory, Research, and Unification. Review of General Psychology, 10(4) 302-317.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.694.6517&rep=rep1&type=pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Taormina, J.R.,Gao,J.H. (2013) Maslow and the Motivation Hierarchy: Measuring Satisfaction of the Needs. American Journal of Psychology, 126(2) 155-177.
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Maslow-and-the-motivation-hierarchy%3A-measuring-of-Taormina-Gao/1e070f0f7075814513324e6a4ee8801257f90dce [Accessed 23 September 2018].
http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0963721409359281 [Accessed 23 September 2018].
McLeod, S. A. (2007) Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs. HCC Certificate in Counselling Skills,1(1) 1-8.
http://highgatecounselling.org.uk/members/certificate/CT2%20Paper%201.pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Money (2018) | Money. [ONLINE] Available at: http://time.com/money/4972232/12-companies-with-the-most-luxurious-employee-perks/. [Accessed 24 September 2018].
Rivera, M.E.K. (2006) Rediscovering the Later Version of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Self-Transcendence and Opportunities for Theory, Research, and Unification. Review of General Psychology, 10(4) 302-317.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.694.6517&rep=rep1&type=pdf [Accessed 23 September 2018].
Taormina, J.R.,Gao,J.H. (2013) Maslow and the Motivation Hierarchy: Measuring Satisfaction of the Needs. American Journal of Psychology, 126(2) 155-177.